“Explore the depths of Fatty Liver causes, symptoms, and discover optimal solutions for maintaining a healthy liver. Gain vital insights into liver health and disease prevention in this comprehensive guide.” Dive into the comprehensive guide on Fatty Liver Disease, exploring causes, symptoms, and effective solutions for optimal liver health. Learn how lifestyle changes, balanced nutrition, and targeted exercises can pave the way to a healthier liver. Empower yourself with insights for a proactive approach to Fatty Liver management.

Fatty Liver: Unlocking Vital Insights: Navigating Fatty Liver Causes, Symptoms, and Solutions for Optimal Liver Health
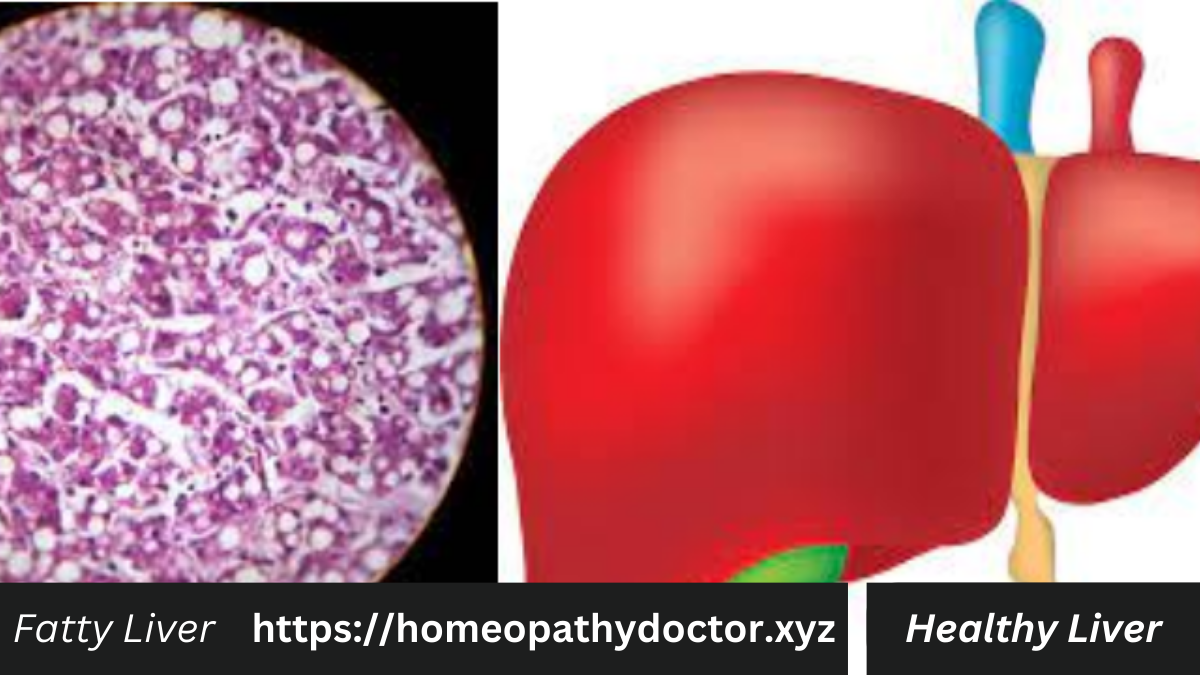
The liver, a silent workhorse in our bodies, plays a crucial role in processing nutrients, detoxifying harmful substances, and maintaining overall well-being. However, the prevalence of Fatty Liver, particularly Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), is on the rise, demanding our attention and proactive measures.
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is a prevalent and potentially serious liver condition characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver cells of individuals who consume little to no alcohol. Representing a spectrum of disorders, NAFLD ranges from simple fatty liver, which is generally benign, to Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH), a more severe form marked by liver inflammation and potential scarring.
A key distinguishing factor of NAFLD is its occurrence in the absence of significant alcohol consumption, making it distinct from alcoholic liver disease. The root causes of NAFLD are often linked to metabolic factors, including obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome. Individuals with diabetes, high blood pressure, or elevated cholesterol levels are at an increased risk.
Early stages of NAFLD may be asymptomatic, emphasizing the importance of routine medical check-ups and liver function tests for timely detection. Lifestyle modifications, including dietary changes, weight management, and regular exercise, form the cornerstone of NAFLD management, underscoring the significance of a holistic approach to liver health.
Understanding Fatty Liver:
Fatty Liver, as the name suggests, occurs when excess fat accumulates in liver cells. While some fat is normal, an excessive buildup can lead to inflammation and impair liver function. Common causes of Fatty Liver include obesity, insulin resistance, high blood sugar, and unhealthy lifestyle choices.
Recognizing Fatty Liver Symptoms:
Early detection is key to managing Fatty Liver effectively. Fatty Liver symptoms might be subtle, ranging from fatigue and abdominal discomfort to more serious indications like jaundice. Being mindful of these signs allows for timely intervention.
Exploring Optimal Solutions for Liver Health:
Maintaining liver health involves adopting lifestyle changes and targeted interventions. A balanced diet, rich in antioxidants and low in saturated fats, can significantly impact liver function. Regular physical activity and weight management also play pivotal roles in preventing and managing Fatty Liver.
Preventing Liver Disease:
Prevention is always preferable to treatment, and this holds true for Fatty Liver. Understanding the causes of Fatty Liver empowers individuals to make informed choices. Adopting a proactive approach to health, including regular check-ups and screenings, can contribute to early detection and intervention.
Navigating Comprehensive Liver Care:
In this comprehensive guide, we delve deep into the intricacies of Fatty Liver, providing vital insights into its causes, symptoms, and optimal solutions for maintaining a healthy liver. By unraveling the mysteries of Fatty Liver, we aim to empower you to make informed decisions about your liver health.
Remember, a healthy liver is a foundation for overall well-being. Take charge of your liver health today, and embark on a journey towards optimal living.
While there conclusive scientific evidence to support the effectiveness of homeopathy in treating specific medical conditions, including Fatty Liver Disease, some individuals explore alternative or complementary approaches. It’s crucial to note that seeking advice from a qualified healthcare professional is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Here’s a general outline of potential homeopathic remedies that individuals may consider, keeping in mind that these should be discussed with a healthcare provider:
Fatty Liver Causes
Fatty Liver Disease, a condition characterized by the excessive accumulation of fat in liver cells, has diverse and interconnected causes. Among the primary Fatty Liver Causes is obesity, which places undue stress on the liver as it processes and stores fats. Insulin resistance, often linked to obesity, further compounds the issue, disrupting the delicate balance of glucose and lipid metabolism in the liver.
Unhealthy dietary habits, particularly the consumption of high levels of saturated fats and refined sugars, contribute significantly to the development of Fatty Liver. Sedentary lifestyles exacerbate these factors, as physical inactivity hinders the body’s ability to metabolize fats effectively.
Genetic predisposition also plays a role, underscoring the importance of personalized approaches in understanding and addressing the roots of Fatty Liver Disease. As we unravel the intricate web of causes, it becomes evident that lifestyle modifications, dietary adjustments, and weight management are pivotal in preventing and managing this prevalent liver condition.
Liver Function
The liver, a vital organ with multifaceted responsibilities, plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. Responsible for detoxifying the blood, metabolizing nutrients, and producing essential proteins, a well-functioning liver is paramount for good health. Regular liver function is an alert to the body’s overall vitality, as it ensures the efficient processing and elimination of toxins.
Monitoring liver function through routine check-ups and blood tests becomes a proactive measure in safeguarding against various liver conditions, including Fatty Liver Disease. Elevated liver enzymes, indicative of potential issues, may serve as early alerts, prompting necessary lifestyle adjustments or medical interventions.
A healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and moderation in alcohol consumption, contributes significantly to optimal liver function. Recognizing the importance of liver health alerts individuals to the interconnectedness of their overall well-being and empowers them to make informed choices for a resilient and thriving body.
Homeopathic Remedies for Fatty Liver Causes:
- Chelidonium majus (Greater Celandine):
- Indicated for liver disorders, especially when there is pain under the right shoulder blade.
- May be considered for individuals with a sluggish liver and jaundice.
- Carduus marianus (Milk Thistle):
- Known for its hepatoprotective properties, supporting liver function.
- May be considered for those with liver congestion and inflammation.
- Nux vomica:
- Often used for individuals with a history of overindulgence in rich foods, alcohol, or stimulants.
- May be considered when there is liver congestion and digestive issues.
- Lycopodium clavatum:
- Indicated for liver conditions associated with bloating and gas.
- May be considered for individuals with a history of overeating.
Consultation with a Homeopathic Practitioner:
Individual responses to homeopathic treatments can vary, and it’s essential to consult with a qualified homeopathic practitioner for personalized advice. Homeopathy considers the individual’s overall health, symptoms, and constitution when recommending remedies. A thorough assessment is necessary to determine the most appropriate course of action.
Liver Health Tips: Promoting optimal liver health involves incorporating mindful choices and adopting habits that support this vital organ’s well-being. Liver health tips serve as invaluable alerts for individuals keen on maintaining a resilient and functional liver. Staying adequately hydrated is a fundamental tip, as water aids in flushing toxins from the body.
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, while low in saturated fats and refined sugars, contributes to liver health by providing essential nutrients and minimizing stress on the organ. Regular physical activity, including both aerobic exercises and strength training, enhances blood circulation and supports the liver’s metabolic functions.
Adequate sleep is another often overlooked but critical aspect of liver health, as the organ undergoes essential repair processes during rest. Additionally, minimizing exposure to environmental toxins and incorporating liver-supportive herbs into one’s diet, such as milk thistle, can complement a healthy lifestyle. Embracing these liver health tips is akin to setting up internal alerts, fostering a proactive and empowered approach to overall well-being.
Complementary Lifestyle Measures:
In addition to homeopathic remedies, individuals should focus on adopting a healthy lifestyle:
- Dietary Changes:
- Emphasize a well-balanced diet with a focus on whole foods.
- Limit intake of processed and high-fat foods.
- Stay hydrated and consider incorporating liver-supportive foods.
- Regular Exercise:
- Engage in regular physical activity to support overall health and weight management.
- Stress Management:
- Incorporate stress-reducing activities, such as meditation or yoga.
Always inform your healthcare provider about any complementary or alternative treatments you are considering, as they can provide guidance and ensure that these approaches align with your overall healthcare plan.
Diagnosing Fatty Liver Disease involves a combination of clinical assessment, medical history review, and diagnostic tests. Here’s an overview of the process:
1. Medical History and Clinical Assessment:
- Symptom Evaluation:
- Discussing symptoms such as fatigue, abdominal discomfort, and potential signs of liver dysfunction.
- Risk Factors:
- Identifying risk factors such as obesity, diabetes, high cholesterol, and metabolic syndrome.
2. Physical Examination:
- Abdominal Examination:
- The healthcare provider may palpate the abdomen to check for liver enlargement or tenderness.
- Jaundice Assessment:
- Examining for signs of jaundice, a yellowing of the skin and eyes associated with liver dysfunction.
3. Blood Tests:
- Liver Function Tests (LFTs):
- Assessing liver enzyme levels (AST, ALT, GGT), bilirubin, and albumin.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC):
- Checking for anemia and other blood-related conditions.
- Blood Glucose and Lipid Profile:
- Evaluating glucose levels and lipid abnormalities, common in individuals with metabolic syndrome.
4. Imaging Studies:
- Ultrasound:
- Often the initial imaging modality, it can visualize liver size, fat content, and identify abnormalities.
- CT Scan or MRI:
- Provides more detailed images of the liver and surrounding structures.
5. Liver Biopsy (In Some Cases):
- Invasive Procedure:
- While less common, a liver biopsy may be recommended to assess the extent of liver damage and inflammation.
- Tissue Examination:
- Examining a small sample of liver tissue under a microscope can provide detailed information about the condition.
6. FibroScan or Transient Elastography:
- Non-Invasive Assessment:
- Measures liver stiffness, helping to assess the degree of liver fibrosis.
7. Clinical Scoring Systems:
- NAFLD Fibrosis Score:
- Utilizes various clinical and laboratory parameters to estimate the likelihood of advanced fibrosis.
- FIB-4 Index:
- Another scoring system based on age, AST, ALT, and platelet count to assess fibrosis risk.
8. Non-Invasive Imaging Modalities:
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) with Proton Density Fat Fraction (PDFF):
- Provides a non-invasive way to quantify liver fat content.
- Controlled Attenuation Parameter (CAP):
- Used in combination with transient elastography to assess liver fat.
Conclusion:
Diagnosing Fatty Liver Disease requires a comprehensive approach, integrating clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. The choice of diagnostic tools depends on the severity of symptoms, risk factors, and the need for further characterization of liver health. Always consult with a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
The treatment of Fatty Liver Disease in allopathic (conventional) medicine generally involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, medication, and management of underlying conditions. It’s important to note that the specific treatment plan can vary based on the severity of the disease, individual health factors, and the presence of any associated conditions. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice. Here’s a general overview:
1. Lifestyle Modifications:
- Dietary Changes:
- Adopting a well-balanced, low-fat diet.
- Limiting or avoiding alcohol consumption.
- Reducing intake of processed and sugary foods.
- Weight Management:
- Gradual weight loss through a combination of diet and exercise.
- Regular Exercise:
- Engaging in regular physical activity to improve insulin sensitivity and overall health.
2. Medications:
- Insulin Sensitizers:
- Medications like pioglitazone may be prescribed to improve insulin sensitivity.
- Lipid-Lowering Medications:
- Statins or other lipid-lowering medications may be used to manage elevated cholesterol levels.
- Antioxidants:
- Vitamin E supplements may be recommended for certain individuals.
- Weight Loss Medications (in some cases):
- Orlistat may be considered for weight management.
3. Management of Underlying Conditions:
- Control of Diabetes:
- Tight control of blood glucose levels for individuals with diabetes.
- Management of Hypertension:
- Control of high blood pressure if present.
- Treatment of Metabolic Syndrome:
- Addressing the components of metabolic syndrome, such as obesity and elevated blood pressure.
4. Regular Monitoring:
- Follow-Up Tests:
- Periodic liver function tests and imaging studies to monitor progress.
- Screening for Complications:
- Assessing for complications such as cirrhosis or liver cancer.
5. Education and Support:
- Patient Education:
- Providing information about the condition, its causes, and the importance of lifestyle changes.
- Supportive Care:
- Offering guidance on maintaining a healthy lifestyle and addressing concerns.
6. Clinical Trials (in certain cases):
- Research Opportunities:
- Participation in clinical trials investigating new treatments for Fatty Liver Disease.
Conclusion: Treatment for Fatty Liver Disease in allopathic medicine focuses on addressing underlying causes, improving liver function, and preventing complications. The approach is comprehensive, involving lifestyle modifications, medications, and ongoing monitoring. Always seek guidance from a qualified healthcare professional for a personalized treatment plan based on individual health needs and circumstances.
While there a specific “cure” for Fatty Liver Disease, lifestyle changes, including dietary modifications and regular exercise, can significantly improve liver health and may even reverse the condition in some cases. Here are dietary and exercise recommendations that may help manage and improve Fatty Liver Disease:
Dietary Recommendations:
Table of Contents
- Low-Fat Diet:
- Focus on a diet low in saturated fats and trans fats.
- Choose lean protein sources, such as poultry, fish, beans, and legumes.
- Limit red meat and processed foods.
- Increased Fiber Intake:
- Incorporate plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Fiber helps with digestion and can contribute to weight management.
- Healthy Fats:
- Include sources of healthy fats, such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil.
- Omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish (e.g., salmon, mackerel) may be beneficial.
- Limit Added Sugars:
- Minimize the intake of sugary beverages, candies, and processed foods.
- Be mindful of hidden sugars in sauces and condiments.
- Control Portion Sizes:
- Practice portion control to manage calorie intake.
- Eating smaller, balanced meals throughout the day can be beneficial.
- Hydration:
- Stay well-hydrated by drinking plenty of water.
- Limit or avoid alcohol consumption.
- Limit Processed Foods:
- Processed foods often contain high levels of unhealthy fats, sugars, and additives.
- Opt for whole, unprocessed foods whenever possible.
Exercise Recommendations:
- Aerobic Exercise:
- Engage in moderate-intensity aerobic exercise for at least 150 minutes per week.
- Activities such as brisk walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming are beneficial.
- Strength Training:
- Include strength training exercises at least two days a week.
- Building muscle can improve insulin sensitivity and support weight management.
- Consistency is Key:
- Establish a regular exercise routine and gradually increase intensity.
- Aim for a combination of cardiovascular and strength-training exercises.
- Lifestyle Activity:
- Incorporate physical activity into daily life, such as taking the stairs or walking instead of driving.
- Yoga or Tai Chi:
- These activities can promote flexibility, reduce stress, and improve overall well-being.
General Lifestyle Tips:
- Weight Management:
- Achieve and maintain a healthy weight through a combination of diet and exercise.
- Gradual Changes:
- Implement changes gradually to make them sustainable over the long term.
- Regular Monitoring:
- Attend regular check-ups and monitor progress through medical tests.
- Stress Reduction:
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques, mindfulness, or activities you enjoy.
It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian before making significant changes to your diet or exercise routine, especially if you have underlying health conditions. They can provide personalized guidance based on your individual health profile.
Features of Fatty Liver Management:
- Dietary Adjustments:
- Opt for a low-fat, high-fiber diet.
- Prioritize fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Include healthy fats like those found in avocados and nuts.
- Limit processed foods, added sugars, and alcohol.
- Exercise Routine:
- Integrate lifestyle activity into daily routines.
- Weight Management:
- Gradual weight loss through a balanced diet and exercise.
- Maintain a healthy weight to improve liver health.
- Hydration:
- Stay well-hydrated with water.
- Limit or avoid alcohol consumption.
- Regular Monitoring:
- Periodic check-ups and medical tests to assess progress.
- Adjust lifestyle based on monitoring results.
- Stress Reduction:
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques.
- Consider activities like yoga or tai chi.
Conclusion:
Fatty Liver Disease management involves a holistic approach combining dietary changes, regular exercise, weight management, and stress reduction. Adopting a low-fat, high-fiber diet along with aerobic and strength training exercises supports overall liver health. Gradual, sustainable lifestyle adjustments, coupled with regular monitoring and professional guidance, contribute to improved well-being. Always consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice and monitoring of your specific health needs.
thanking and credit for images free google